Speed, efficiency, and flexibility.
These are the three things that every industrial and manufacturing organization around the world has always wanted and needed.
How to get it, however, has changed dramatically, especially since the widespread adoption of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). For most industrial and manufacturing organizations, connectivity is no longer new, it’s necessary.
But, like the technology itself, industrial plant connectivity, too, must continue to evolve and mature. Fortunately, technology itself is making it easier to do so. And leading the way? The BACnet interoperability protocol.
Here’s a look at how industrial and manufacturing organizations like yours can capitalize on technological advancements, smart devices, and the best-in-class open protocol, BACnet, to take operations to higher levels of speed, efficiency, and flexibility.
What Is the BACnet Protocol?
The BACnet, or Building Automation Control Networks, protocol is a leading open communications protocol that’s been deployed with more than 25 million devices globally.
BACnet was developed in 1987 and has since been continuously managed and updated by the BACnet Committee of the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE).
Its purpose? To enable interoperability within a facility’s Building Management System (BMS) or Building Automation System (BAS).
What’s BACnet Got to Do with Industrial Automation?
If you’re wondering what the BACnet protocol means for industrial automation, the answer is simple: Everything.
It answers the question: How can we pull critical data from our BMS or BAS and put it into our industrial automation systems so we can optimize manufacturing and production?
The BACnet protocol is the mechanism by which an interoperable system exchanges information—regardless of the type and number of services it performs. In other words, it plays a major role in ensuring efficient and profitable operations.
Of course, BACnet can’t do it alone. Smart devices, such as temperature sensors, along with a protocol translating gateway like MSA FieldServer, are needed to bring disparate devices, legacy systems, and the BMS or BAS together with the industrial automation system.
It’s here where the magic happens. As an example, if you’re an ice cream manufacturing plant and the building is too warm, that’s a major problem. But with a BACnet-enabled automated plant equipped with a FieldServer gateway, problem solved. Automatically and seamlessly, the connected system alerts personnel and also changes or shuts down production until temperatures are back to normal.
The value comes from knowing when and where something has occurred that could be concerning or catastrophic.
BACnet-Supported Applications
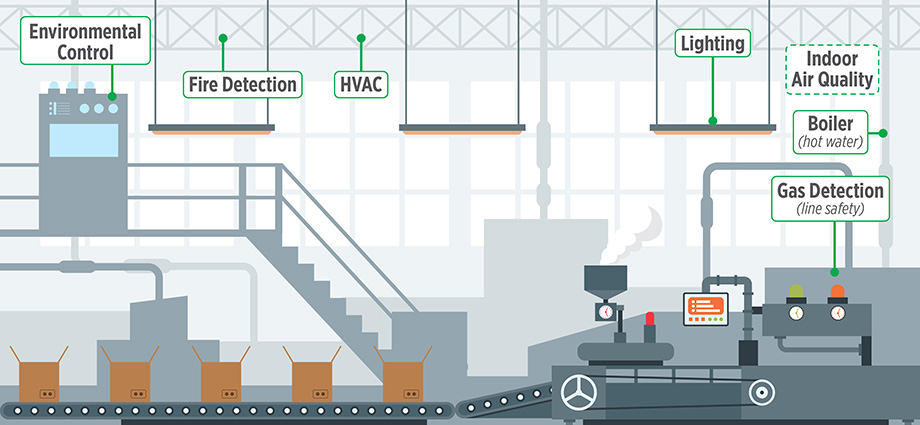
Because it is so prevalent, BACnet is found virtually everywhere, making it critical for industrial plants to run efficiently.
Within the context of interoperability between facility and production, BACnet-enabled automation solutions provide critical information needed to streamline processes and optimize production within these five key areas:
- Fire Alarm Panels: alerts, lights, sounds, evacuations
- Lighting: occupancy levels and emergency egress
- HVAC: temperature and fan adjustments
- Environmental Control: air quality
- Energy Management: power consumption and energy savings
BACnet + Other Protocols
Although BACnet is the primary protocol standard for automation, not all device manufacturers use it. And that’s okay—as long as you have a protocol gateway that can help your disparate devices talk to each other.
Our FieldServer gateway, for example, speaks and converts more than 140 protocols so you can unlock valuable information from both your building and industrial automation systems.
Because it’s a plug-and-play solution that easily integrates with BACnet Networks (BACnet/IP & BACnet MS/TP), FieldServer enables real-time, contextualized intelligence across both your building and industrial automation systems.
To learn more or schedule a demo, talk with an MSA Representative today.



